MF flat sheet
The selection of microfiltration flat sheet membranes from Alfa Laval covers different pore sizes and flux properties. The membranes are used in an extensive range of processes applied in the food, beverage, dairy, biotech and pharmaceutical industries
Alfa Laval offers two series of microfiltration (MF) membranes with different pore sizes and flux properties. The membrane materials are either polysulphone polymer or fluoro polymer based on a unique construction on polypropylene (PP) support material which provides optimum cleaning conditions.
MFG series
The MFG microfiltration membrane is made of polysulphone polymer. The membrane is available in the following types: MFG 1 having a pore size of 0.1 µm and MFG 2 with a pore size of 0.2 µm.
MFP series
The MFP microfiltration membrane is made of fluoro polymer. The membrane is available in the types: MFP 2 (pore size 0.2 µm), MFP 5 (0.5 µm) and finally MFP 8 (0.8 µm).
Benefits
- cover a broad spectrum of flux properties, pore sizes, molecular weight cut-off values and rejection capabilities
- available by the metre, as standard 20 x 20 cm sheets or cut into flat sections to fit into all Alfa Laval plate-and-frame module configurations
- delivered with necessary lock and passage rings
- suitable for extensive range of processes
- manufactured by Alfa Laval's own membrane centre
Sådan fungerer det
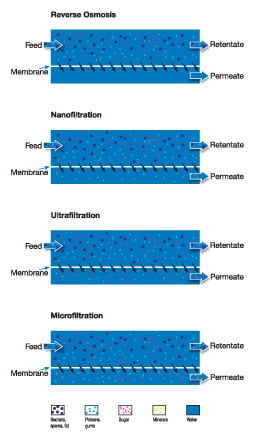
Reverse osmosis (RO)
RO uses the tightest possible membrane in liquid separation. In principle, water is the only material that can permeate the membrane. All other materials (salts, sugars, etc.) will be unable to pass through.
Nanofiltration (NF)
NF is not as fine a separation process as reverse osmosis, and uses membranes that are slightly more open. Nanofiltration allows small ions to pass through while excluding larger ions and most organic components.
Ultrafiltration (UF)
UF involves using membranes in which the pores are larger and the pressure is relatively low. Salts, sugars, organic acids and smaller peptides are allowed to pass, while proteins, fats and polysaccharides are not.
Microfiltration (MF)
In MF, suspended solids, bacteria and fat globules are normally the only substances not allowed to pass through.

